🔥🔥🔥धातु और अधातु🔥🔥🔥 |
Metals and Non-Metals – Class 10 Science
📘📘📘📘📘📘📘📘📘📘📘📘📘📘📘📘📘📘📘
CHALO INTRO DETE HAI PEHLE METAL AND NON METAL KA-----------
## 🔹💁 *परिचय | Introduction*
धातु और अधातु हमारे चारों ओर पाए जाने वाले सबसे महत्वपूर्ण तत्वों में से हैं। इनका प्रयोग घर, स्कूल, उद्योग और चिकित्सा क्षेत्र तक फैला हुआ है।
*Metals and non-metals are among the most important elements found around us. They are used in homes, schools, industries, and even in medicine.*
DEKHTE HAI METAL KI DIFINATION KYA HOGI?
## 🔹💁 *धातु क्या होते हैं? |
## What are Metals ? *
धातु वे तत्व होते हैं जो सामान्यतः ठोस, कठोर, चमकदार होते हैं और गर्मी व बिजली के अच्छे सुचालक होते हैं।
*Metals are elements that are usually solid, hard, shiny, and good conductors of heat and electricity.*
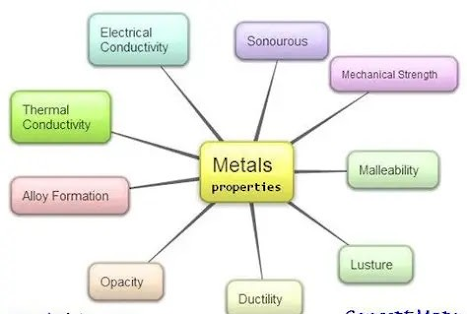
### ✔️ 💁*धातुओं की विशेषताएँ |
### Properties of Metals:*
* कठोर होती हैं (Hard)
* चमकदार होती हैं (Lustrous)
* तन्य होती हैं (Ductile – can be drawn into wires)
* नमी योग्य होती हैं (Malleable – can be hammered into sheets)
* बिजली और गर्मी की सुचालक होती हैं (Good conductors of heat and electricity)
* ध्वनि को पार करती हैं (Sonorous – produce sound when struck)
*Metals are hard, lustrous, ductile, malleable, sonorous, and good conductors of heat and electricity.*
---
## 🧪💁 *धातुओं के उदाहरण | Examples of Metals*
| धातु | संकेत | उपयोग |
| ---------------------------------------| -----------------------------| ------------------------------------ |
| लोहा (Iron) | Fe | निर्माण कार्य, पुल, मशीनें |
| तांबा (Copper) | Cu | तारों में |
| एल्युमिनियम (Aluminium) | Al | हवाई जहाज, बर्तन |
| चाँदी (Silver) | Ag | विद्युत सुचालक, आभूषण |
| सोना (Gold) | Au | आभूषण |
| टंगस्टन (Tungsten) | W | बल्ब का फिलामेंट |
| पारा (Mercury) | Hg | थर्मामीटर (द्रव धातु) |
| जिंक (Zinc) | Zn | जंग से सुरक्षा देने के लिए (गैल्वनाइजेशन) |
---
DEKHTE HAI NON-METAL KI DIFINATION KYA HOGI?
## 🔸💁 *अधातु क्या होते हैं? |
What are Non-Metals ?
अधातु वे तत्व होते हैं जो धातुओं की विशेषताओं को नहीं दर्शाते। ये सामान्यतः नरम, भंगुर और कुचालक होते हैं।
*Non-metals are elements that do not exhibit the typical properties of metals. They are usually soft, brittle, and poor conductors.*
###
📘💁*अधातुओं की विशेषताएँ |
Properties of Non-Metals:*
* भंगुर होती हैं (Brittle – break easily)
* तन्यता और नमी योग्य नहीं होतीं (Not ductile or malleable)
* कुचालक होती हैं (Poor conductors of heat and electricity)
* ज़्यादातर अधातु गैस रूप में होती हैं (Mostly gaseous in nature)
* चमक नहीं होती (Dull appearance)
*Non-metals are brittle, non-ductile, non-malleable, poor conductors, mostly gases, and dull.*
---
## 🧪 💁*अधातुओं के उदाहरण |
Examples of Non-Metals*
| अधातु | संकेत | उपयोग |
| ---------------------------- | ------------------------------------- | --------------------------- |
| ऑक्सीजन (Oxygen) | O₂ | श्वसन प्रक्रिया |
| नाइट्रोजन (Nitrogen) | N₂ | उर्वरक |
| हाइड्रोजन (Hydrogen) | H₂ | ईंधन |
| क्लोरीन (Chlorine) | Cl₂ | जल शुद्धिकरण |
| सल्फर (Sulfur) | S | दवाइयाँ, बारूद |
| कार्बन (Carbon) | C | ईंधन, हीरा, ग्रेफाइट |
| आयोडीन (Iodine) | I | दवा में प्रयोग |
---
##
📘 💁*धातु और अधातु में अंतर | Difference Between Metals and Non-Metals*
| विशेषता (Property) | धातु (Metals) | अधातु (Non-Metals) |
| ---------------------------------- | -------------------------------- | --------------------------------- |
| अवस्था (State) | ठोस (Solid) | गैस, ठोस या द्रव |
| चमक (Shine) | होती है | नहीं होती |
| सुचालकता (Conductivity) | अच्छी | खराब |
| तन्यता (Ductility) | होती है | नहीं होती |
| नमी योग्य (Malleable) | होती है | नहीं होती |
| ध्वनि (Sonorous) | ध्वनि निकालती हैं | नहीं निकालतीं |
---
## 🔧💁 *उपयोग |
## Uses*
### ➤💁 *धातुओं के उपयोग |
### Uses of Metals:*
* विद्युत तारों में (Copper, Aluminium)
* बर्तनों और निर्माण कार्य में (Iron, Steel)
* हवाई जहाज और गाड़ियों में (Aluminium, Steel)
* आभूषणों में (Gold, Silver)
* मशीनों और औजारों में (Iron)
### ➤ 💁*अधातुओं के उपयोग |
### 💁Uses of Non-Metals:*
* ऑक्सीजन – श्वसन के लिए
* नाइट्रोजन – खाद (fertilizer) में
* क्लोरीन – पानी की सफाई में
* सल्फर – औषधियों और पटाखों में
* ग्रेफाइट – पेंसिल और बिजली के ब्रश में
* आयोडीन – घावों पर लगाने वाली दवा
---
## ❓ 💁*अतिरिक्त प्रश्न–उत्तर |
💁Extra Questions and Answers*
*Q1. कौन-सी धातु द्रव होती है?*
👉 पारा (Mercury – Hg) एकमात्र द्रव धातु है।
*Mercury is the only metal that is liquid at room temperature.*
*Q2. सबसे कठोर धातु कौन सी है?*
👉 टंगस्टन (Tungsten – W)
*Tungsten is the hardest metal.*
*Q3. कौन सी अधातु बिजली की सुचालक है?*
👉 ग्रेफाइट (Graphite – कार्बन का एक रूप)
*Graphite is a good conductor of electricity though it is a non-metal.*
*Q4. कौन सी अधातु ठोस रूप में होती है?*
👉 कार्बन, आयोडीन और सल्फर
*Carbon, iodine, and sulfur are solid non-metals.*
*Q5. सबसे कठोर अधातु कौन-सी है?*
👉 हीरा (Diamond – कार्बन का रूप)
*Diamond (a form of carbon) is the hardest known natural substance.*
*Q6. किस अधातु का उपयोग जल शुद्ध करने में होता है?*
👉 क्लोरीन
*Chlorine is used to purify water.*
*Q7. किस धातु का प्रयोग हवाई जहाज में होता है?*
👉 एल्युमिनियम
*Aluminium is used in making aircraft due to its lightweight and strength.*
📘 अयस्क क्या है? | What is an Ore?
अयस्क वह प्राकृतिक खनिज होता है जिसमें धातु या धातु-युक्त यौगिक इस मात्रा में पाए जाते हैं कि उन्हें आर्थिक रूप से लाभदायक तरीके से निकाला जा सके।
हर खनिज अयस्क नहीं होता, लेकिन हर अयस्क एक खनिज होता है।
🔹 उदाहरण:
-
बॉक्साइट (Bauxite) – एल्युमिनियम का अयस्क
-
हैमेटाइट (Hematite) – लोहे का अयस्क
-
सिनाबर (Cinnabar) – पारे (Mercury) का अयस्क
-
गैलैना (Galena) – सीसा (Lead) का अयस्क
🔹 अयस्क से धातु प्राप्त करने की प्रक्रिया को "धातु निष्कर्षण" (Metallurgy) कहते हैं। इसमें निम्नलिखित चरण होते हैं:
-
अयस्क को पीसना (Crushing)
-
अशुद्धियाँ (Gangue) हटाना
-
उपयुक्त विधि से धातु को निकालना (जैसे: तापीय अपचयन, विद्युत अपघटन, आदि)
An ore is a naturally occurring mineral from which a metal or metallic compound can be extracted profitably and easily.
Every ore is a mineral, but not every mineral is an ore.
🔹 Examples:
-
Bauxite – Ore of Aluminium
-
Hematite – Ore of Iron
-
Cinnabar – Ore of Mercury
-
Galena – Ore of Lead
🔹 The process of obtaining metal from ore is called metallurgy, and it involves three major steps:
-
Crushing the ore
-
Removing impurities (Gangue)
-
Extracting the metal by suitable chemical methods (like reduction, electrolysis, etc.)
अयस्क और खनिज में अंतर | Difference between Ore and Mineral
| क्रम | अयस्क (Ore) | खनिज (Mineral) |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | जिससे धातु को लाभदायक तरीके से निकाला जा सकता है | प्रकृति में पाई जाने वाली धात्विक/अधात्विक ठोस पदार्थ |
| 2️⃣ | धातु की मात्रा अधिक होती है | धातु हमेशा मौजूद नहीं होती |
| 3️⃣ | उदाहरण: बॉक्साइट, हेमेटाइट | उदाहरण: क्वार्ट्ज़, कैल्साइट |
🔹💁बहुविकल्पीय प्रश्न (Multiple Choice Questions - MCQs)
-
निम्न में से कौन-सी एक अधातु है?
Which one of the following is a non-metal?
A. लोहा (Iron)
B. सोना (Gold)
C. गंधक (Sulphur)
D. ताँबा (Copper)
✅ सही उत्तर: गंधक (Sulphur) -
धातु जल से अभिक्रिया करके क्या बनाती है?
What do metals form when they react with water?
A. अम्ल (Acid)
B. हाइड्रोजन गैस (Hydrogen gas)
C. कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड (Carbon dioxide)
D. नाइट्रोजन (Nitrogen)
✅ सही उत्तर: हाइड्रोजन गैस (Hydrogen gas) कौन-सी धातु इतनी नरम होती है कि चाकू से काटी जा सकती है?
Which of the following metals is so soft that it can be cut with a knife?
A. लोहा (Iron)
B. ताँबा (Copper)
C. सोडियम (Sodium)
D. एल्यूमिनियम (Aluminium)
✅ सही उत्तर: सोडियम (Sodium)4. निम्न में से कौन-सी अधातु बिजली का सुचालक है?
Which of the following non-metals is a good conductor of electricity?
A. गंधक (Sulphur)
B. फास्फोरस (Phosphorus)
C. ग्रेफाइट (Graphite)
D. क्लोरीन (Chlorine)
✅ सही उत्तर: ग्रेफाइट (Graphite)5. निम्न में से कौन-सा एक धातु ऑक्साइड अम्लीय नहीं होता है?
Which of the following metal oxides is not acidic?
A. ZnO
B. CuO
C. Na2O
D. SO2
✅ सही उत्तर: SO₂ (यह धातु ऑक्साइड नहीं, अधातु ऑक्साइड है)6. निम्न में से कौन-सा धातु जल से अभिक्रिया नहीं करता है?
Which of the following metals does not react with water?
A. सोडियम (Sodium)
B. कैल्शियम (Calcium)
C. मैग्नीशियम (Magnesium)
D. ताँबा (Copper)
✅ सही उत्तर: ताँबा (Copper)7. अधातु जो जलाने पर नीली लौ देता है:
Which non-metal gives a blue flame when burnt?
A. फास्फोरस (Phosphorus)
B. सल्फर (Sulphur)
C. क्लोरीन (Chlorine)
D. कार्बन (Carbon)
✅ सही उत्तर: सल्फर (Sulphur)8. कौन-सा एक अम्फोटेरिक ऑक्साइड है?
Which one is an amphoteric oxide?
A. MgO
B. Na2O
C. Al2O3
D. SO3
✅ सही उत्तर: Al₂O₃ (एलुमिनियम ऑक्साइड)9. कौन-सी अधातु गैस अवस्था में पाई जाती है?
Which of the following non-metals is found in gaseous state?
A. आयोडीन (Iodine)
B. सल्फर (Sulphur)
C. क्लोरीन (Chlorine)
D. फास्फोरस (Phosphorus)
✅ उत्तर / Answer: क्लोरीन (Chlorine)10. निम्न में से कौन-सा पदार्थ धातु और अधातु दोनों के गुण दर्शाता है?
Which of the following shows properties of both metals and non-metals?
A. जिंक (Zinc)
B. कार्बन (Carbon)
C. सिलिकॉन (Silicon)
D. लोहा (Iron)
✅ उत्तर / Answer: सिलिकॉन (Silicon)11. कौन-सा अधातु जल के साथ प्रतिक्रिया नहीं करता?
Which non-metal does not react with water?
A. कार्बन (Carbon)
B. क्लोरीन (Chlorine)
C. सल्फर (Sulphur)
D. सभी (All of these)
✅ उत्तर / Answer: सभी (All of these)12. कौन-सी धातु कमरे के तापमान पर तरल अवस्था में होती है?
Which metal is liquid at room temperature?
A. सोना (Gold)
B. लोहा (Iron)
C. पारा (Mercury)
D. ताँबा (Copper)
✅ उत्तर / Answer: पारा (Mercury)13. किस अधातु का उपयोग विस्फोटकों में किया जाता है?
Which non-metal is used in explosives?
A. क्लोरीन (Chlorine)
B. नाइट्रोजन (Nitrogen)
C. ऑक्सीजन (Oxygen)
D. हाइड्रोजन (Hydrogen)
✅ उत्तर / Answer: नाइट्रोजन (Nitrogen)14. निम्न में से कौन-सी धातु सबसे अभिक्रियाशील है?
Which of the following is the most reactive metal?
A. लोहा (Iron)
B. ताँबा (Copper)
C. सोडियम (Sodium)
D. जिंक (Zinc)
✅ उत्तर / Answer: सोडियम (Sodium)15. कौन-सी धातु शरीर के लिए आवश्यक पोषक तत्व है?
Which metal is an essential nutrient for the human body?
A. सीसा (Lead)
B. जिंक (Zinc)
C. मरकरी (Mercury)
D. सोना (Gold)
✅ उत्तर / Answer: जिंक (Zinc)CHALO AB KUCH SHORT QUESTION JO EXAM ME IMPORTANT HOTE H.🔹
💁Short Answer Questions with Answers
1. दो भौतिक गुण लिखिए जो केवल धातुओं में पाए जाते हैं।
Q. Write any two physical properties that are shown only by metals.
✍️ उत्तर / Answer:
-
धातुएँ चमकीली होती हैं (Metals are lustrous).
-
वे तन्य होती हैं, यानी उन्हें पतली चादियों में बदला जा सकता है (They are malleable).
2. तन्यता (Malleability) से आप क्या समझते हैं?
Q. What do you understand by malleability?
✍️ उत्तर / Answer:
तन्यता वह गुण है जिसके द्वारा किसी धातु को हथौड़े से पीटकर पतली चादियों में बदला जा सकता है।
Malleability is the property by which a metal can be beaten into thin sheets.3. अधातु आमतौर पर विद्युत के सुचालक क्यों नहीं होते?
Q. Why are non-metals generally poor conductors of electricity?
✍️ उत्तर / Answer:
अधातुओं में मुक्त इलेक्ट्रॉन नहीं होते, जिससे वे विद्युत का संचालन नहीं कर पाते।
Non-metals do not have free electrons, so they cannot conduct electricity.4. धातु जल के साथ प्रतिक्रिया करके क्या बनाती हैं?
Q. What do metals form when they react with water?
✍️ उत्तर / Answer:
वे हाइड्रोजन गैस और धातु हाइड्रॉक्साइड बनाते हैं।
They form hydrogen gas and metal hydroxide.5. अम्फोटेरिक ऑक्साइड किसे कहते हैं? एक उदाहरण दीजिए।
Q. What is an amphoteric oxide? Give one example.
✍️ उत्तर / Answer:
ऐसे ऑक्साइड जो अम्ल और क्षार दोनों के साथ अभिक्रिया करते हैं उन्हें अम्फोटेरिक ऑक्साइड कहते हैं।
उदाहरण: Al₂O₃ (एलुमिनियम ऑक्साइड)
Amphoteric oxides react with both acids and bases. Example: Al₂O₃ (Aluminium oxide)6. कोई दो धातु लिखिए जो अत्यधिक अभिक्रियाशील होती हैं।
Q. Name any two metals which are highly reactive.
✍️ उत्तर / Answer:
सोडियम (Sodium) और पोटैशियम (Potassium)
Sodium and Potassium7. ताँबे और लोहा में कौन अधिक सक्रिय है? कैसे पता करेंगे?
Q. Which is more reactive – copper or iron? How will you find out?
✍️ उत्तर / Answer:
लोहा अधिक सक्रिय है। यदि हम ताँबे के सल्फेट में लोहे की कील डालते हैं तो ताँबा जम जाता है, यह दर्शाता है कि लोहा ताँबे से अधिक सक्रिय है।
Iron is more reactive. When an iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate, copper gets displaced, showing iron is more reactive.8. अधातु जल और अम्ल के साथ क्यों प्रतिक्रिया नहीं करते?
Q. Why do non-metals not react with water and acids?
✍️ उत्तर / Answer:
क्योंकि अधातुओं में ऐसे गुण नहीं होते कि वे हाइड्रोजन गैस उत्पन्न करें या सक्रिय प्रतिक्रिया दें।
Because non-metals do not have the ability to produce hydrogen gas or show active chemical reactivity with water or acids.9. धातुओं का उपयोग विद्युत तारों में क्यों किया जाता है?
Q. Why are metals used for making electrical wires?
✍️ उत्तर / Answer:
क्योंकि धातुएँ अच्छे विद्युत चालक होती हैं और तन्य होती हैं।
Because metals are good conductors of electricity and ductile.10. जंग लगना क्या है? इसे रोकने के दो उपाय बताइए।
Q. What is rusting? Write any two methods to prevent it.
✍️ उत्तर / Answer:
जब लोहा हवा और नमी के संपर्क में आता है तो वह जंग खा जाता है, इसे जंग लगना (rusting) कहते हैं।
रोकथाम के उपाय (Methods to prevent rusting):-
पेंट करना (Painting)
-
गैल्वेनाइजेशन करना (Galvanizing)
-
CHALO AB KUCH LONG QUESTION JO EXAM ME IMPORTANT HOTE HAI.
🔷 💁Long Answer Type Questions with Answers
🔶 Q1. Explain the physical properties of metals and non-metals with examples. / धातु और अधातु के भौतिक गुणों को उदाहरण सहित समझाइए।
Answer / उत्तर:
Metals are generally hard, shiny (lustrous), good conductors of heat and electricity, ductile (can be drawn into wires), and malleable (can be hammered into thin sheets). Examples include iron, copper, and aluminium. Metals also produce a ringing sound when struck – they are sonorous. Most metals are solid at room temperature, except mercury which is a liquid.
Non-metals, on the other hand, are usually soft (except diamond), dull (non-lustrous), poor conductors of heat and electricity (except graphite), and neither ductile nor malleable – they break when hammered. Non-metals do not produce any sound and are non-sonorous. They may exist in solid, liquid, or gaseous form. Examples include sulphur, phosphorus, and oxygen.
These differences are essential in deciding the uses of metals and non-metals in real life – for example, metals in wiring and cooking, and non-metals like oxygen for breathing.
धातु सामान्यतः कठोर, चमकीली, अच्छे ताप और विद्युत चालक, तन्य और तन्यशील होती हैं। उदाहरण: लोहा, ताँबा, एल्यूमिनियम। जब इन्हें ठोंका जाता है, तो ये ध्वनि करती हैं – अर्थात् सोनोरस होती हैं। अधिकांश धातु कमरे के तापमान पर ठोस होती हैं, केवल पारा तरल होता है।
अधातु आमतौर पर मुलायम होती हैं (हीरा छोड़कर), चमकहीन, खराब चालक (ग्रेफाइट को छोड़कर), और न तो तन्य होती हैं और न ही तन्यशील – ठोंकने पर टूट जाती हैं। अधातु ध्वनि नहीं करतीं। ये ठोस, द्रव या गैस रूप में हो सकती हैं। उदाहरण: गंधक, फास्फोरस, ऑक्सीजन।
यही गुण इनके प्रयोग को तय करते हैं – जैसे धातु तार व बर्तन में और अधातु श्वसन व उर्वरकों में।
🔶 Q2. What is corrosion? What are its causes and prevention methods? / जंग लगना क्या है? इसके कारण व रोकथाम के उपाय क्या हैं?
Answer / उत्तर:
Corrosion is a slow chemical process in which metals react with moisture, air, water, or other chemicals from the environment and get gradually destroyed. One common example is the rusting of iron. When iron comes in contact with water and oxygen, it forms a reddish-brown flaky substance called rust (iron oxide).
Causes of Corrosion:
-
Presence of moisture and oxygen
-
Acidic gases in the atmosphere
-
Saline water
-
Pollutants and chemicals
Prevention Methods:
-
Painting the metal surface to prevent exposure to air and moisture.
-
Galvanization, in which a layer of zinc is applied to iron objects.
-
Oiling or greasing prevents moisture contact.
-
Alloying iron with chromium or nickel to make stainless steel, which resists corrosion.
हिंदी में:
जंग लगना एक धीमी रासायनिक प्रक्रिया है जिसमें धातुएँ वातावरण की नमी, ऑक्सीजन, जल या रसायनों से अभिक्रिया कर क्षतिग्रस्त हो जाती हैं। सबसे सामान्य उदाहरण लोहा है। जब यह पानी और ऑक्सीजन के संपर्क में आता है तो लाल-भूरी पपड़ी जैसा पदार्थ बनता है जिसे हम जंग (आयरन ऑक्साइड) कहते हैं।
कारण:
-
नमी और ऑक्सीजन की उपस्थिति
-
अम्लीय गैसें
-
खारा पानी
-
प्रदूषण
रोकथाम:
-
पेंटिंग करके धातु की सतह को सुरक्षित करना
-
जस्तीकरण (Galvanization)
-
तेल या ग्रीस लगाना
-
मिश्रधातु बनाकर जैसे स्टेनलेस स्टील
🔶 Q3. Explain the chemical properties of metals with proper examples. / धातुओं के रासायनिक गुणों को उदाहरण सहित समझाइए।
Answer / उत्तर:
Metals show specific chemical properties:
-
Reaction with Oxygen:
Metals react with oxygen to form basic metal oxides.
Example:
-
Reaction with Water:
Some metals like sodium and potassium react vigorously with water forming metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Example:
-
Reaction with Acids:
Metals react with dilute acids to produce salt and hydrogen gas.
Example:
-
Displacement Reactions:
More reactive metals displace less reactive ones from their salt solutions.
Example:
हिंदी में:
धातुओं के मुख्य रासायनिक गुण निम्नलिखित हैं:
-
ऑक्सीजन से अभिक्रिया:
धातुएँ ऑक्सीजन से मिलकर क्षारीय ऑक्साइड बनाती हैं।
उदाहरण:
-
जल से अभिक्रिया:
सोडियम और पोटैशियम जैसे धातु जल से तेज़ प्रतिक्रिया करके धातु हाइड्रॉक्साइड और हाइड्रोजन गैस बनाते हैं।
-
अम्ल से अभिक्रिया:
धातु तनु अम्ल से अभिक्रिया करके लवण और हाइड्रोजन गैस बनाते हैं।
-
विस्थापन अभिक्रिया:
अधिक सक्रिय धातु कम सक्रिय धातु को उसके लवण से विस्थापित कर सकती है।
🔶 Q4. Describe how the reactivity series is used in displacement reactions. / अभिक्रियाशीलता श्रेणी का विस्थापन अभिक्रियाओं में कैसे प्रयोग किया जाता है?
Answer / उत्तर:
The Reactivity Series is a list of metals arranged in the decreasing order of their reactivity. It helps us predict whether a displacement reaction will occur or not.
In a displacement reaction, a more reactive metal will replace a less reactive metal from its salt solution.
Example:
When zinc (Zn) is placed in a copper sulphate solution (CuSO₄), zinc displaces copper because zinc is more reactive.
But if copper is placed in zinc sulphate, no reaction occurs as copper is less reactive.
This concept is useful in:
-
Metal extraction
-
Designing chemical batteries
-
Predicting corrosion
हिंदी में:
अभिक्रियाशीलता श्रेणी में धातुओं को उनकी रासायनिक सक्रियता के घटते क्रम में रखा जाता है। इससे हमें यह अनुमान लगाने में मदद मिलती है कि कोई विस्थापन अभिक्रिया होगी या नहीं।
विस्थापन अभिक्रिया में अधिक सक्रिय धातु, कम सक्रिय धातु को उसके लवण से विस्थापित कर देती है।
उदाहरण:
जब जिंक को कॉपर सल्फेट के विलयन में डाला जाता है:
लेकिन यदि कॉपर को जिंक सल्फेट में डालें, तो कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं होती।
यह श्रेणी उपयोगी है:
-
धातुओं के निष्कर्षण में
-
बैटरियों के निर्माण में
-
जंग की भविष्यवाणी में
🔶 Q5. Explain why non-metals do not conduct electricity and give one exception. / अधातु विद्युत का संचालन क्यों नहीं करते? एक अपवाद बताइए।
Answer / उत्तर:
Non-metals generally do not conduct electricity because they do not have free electrons. Electricity requires the movement of electrons or ions. In non-metals, the electrons are tightly held to the nucleus and cannot move freely.
Exception – Graphite:
Graphite is a form of carbon and a non-metal. But it conducts electricity. This is because in graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to only three other carbon atoms. The fourth electron is free to move and conducts electricity.
Applications of Graphite:
-
Used in electrodes of batteries
-
Used in electric arc furnaces
हिंदी में:
अधातु विद्युत का संचालन नहीं करते क्योंकि उनमें मुक्त इलेक्ट्रॉनों की कमी होती है। विद्युत प्रवाह के लिए मुक्त इलेक्ट्रॉन आवश्यक होते हैं, जबकि अधातुओं में इलेक्ट्रॉन न्यूक्लियस से जुड़े होते हैं और स्वतंत्र रूप से गति नहीं कर सकते।
अपवाद – ग्रेफाइट:
ग्रेफाइट, जो कि कार्बन का एक रूप है, विद्युत का सुचालक है। इसमें प्रत्येक कार्बन परमाणु तीन अन्य से जुड़ा होता है और एक इलेक्ट्रॉन स्वतंत्र होता है, जो विद्युत का संचालन करता है।
प्रयोग:
-
बैटरियों में इलेक्ट्रोड
-
विद्युत चाप भट्टियों में
🔶 Q6. What is an alloy? How are alloys better than pure metals? / मिश्रधातु क्या होती है? ये शुद्ध धातुओं से बेहतर कैसे होती हैं?
Answer / उत्तर:
An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal. It is made to improve the properties of the base metal.
Examples of alloys:
-
Brass = Copper + Zinc
-
Bronze = Copper + Tin
-
Steel = Iron + Carbon
Advantages of alloys over pure metals:
-
Stronger than pure metals (e.g., steel is stronger than iron)
-
Resist corrosion (e.g., stainless steel)
-
Better appearance and finishing
-
Improved hardness and strength
Alloys are used in construction, machinery, transportation, and kitchen tools.
हिंदी में:
मिश्रधातु दो या दो से अधिक धातुओं, या एक धातु और एक अधातु का समांग मिश्रण होती है। इसका निर्माण धातु के गुणों को सुधारने के लिए किया जाता है।
उदाहरण:
-
पीतल = ताँबा + जस्ता
-
कांसा = ताँबा + टिन
-
स्टील = लोहा + कार्बन
मिश्रधातुओं के लाभ:
-
ये शुद्ध धातुओं से अधिक मज़बूत होती हैं।
-
इन पर जंग नहीं लगती (जैसे स्टेनलेस स्टील)।
-
इनमें चमक व सुंदरता होती है।
-
कठोरता व मजबूती अधिक होती है।
इनका उपयोग निर्माण, मशीनें, वाहनों व रसोई के बर्तनों में होता है।
🔶 Q7. Explain the process of corrosion. What are the methods to prevent it? / जंग लगने की प्रक्रिया को समझाइए। इसे रोकने के उपाय बताइए।
Answer / उत्तर:
Corrosion is the process where metals react with environmental elements like moisture, air, or acids, leading to their deterioration. The most common example is rusting of iron.
Rusting Reaction:
When iron reacts with oxygen and water:
This forms hydrated iron oxide, commonly called rust.
Effects of Corrosion:
-
Weakens the metal
-
Damages buildings, bridges, and machines
-
Economic loss due to maintenance
Methods to prevent corrosion:
-
Galvanization – Coating iron with zinc.
-
Painting – A protective layer on the metal surface.
-
Oiling and greasing – Prevents moisture contact.
-
Alloying – Using stainless steel (iron + chromium) prevents rust.
-
Electroplating – Covering with a less reactive metal.
हिंदी में:
जंग लगना (Corrosion) एक ऐसी प्रक्रिया है जिसमें धातु वातावरण में मौजूद नमी, ऑक्सीजन और अन्य गैसों के साथ प्रतिक्रिया करती है और धीरे-धीरे नष्ट हो जाती है।
जंग की अभिक्रिया (Iron के लिए):
जब लोहा ऑक्सीजन और जल के संपर्क में आता है:
यह अभिक्रिया लौह ऑक्साइड (जंग) बनाती है।
प्रभाव:
-
धातु की मजबूती कम हो जाती है
-
मशीन, पुल और इमारतें कमजोर हो जाती हैं
-
मरम्मत में आर्थिक नुकसान होता है
रोकथाम के उपाय:
-
गैल्वनाइजेशन – लोहे पर जस्ता की परत
-
पेंटिंग – सतह पर पेंट चढ़ाना
-
चिकनाई लगाना – तेल या ग्रीस लगाना
-
मिश्रधातु बनाना – जैसे स्टेनलेस स्टील
-
विद्युतलेपन (Electroplating) – किसी कम अभिक्रियाशील धातु की परत चढ़ाना
🔶 Q8. Describe the steps involved in the extraction of metals from their ores. / अयस्कों से धातुओं के निष्कर्षण की प्रक्रिया को समझाइए।
Answer / उत्तर:
The process of extracting metals from ores involves several steps:
-
Concentration of Ore:
Unwanted materials (gangue) are removed. Methods include gravity separation, froth flotation, magnetic separation. -
Calcination or Roasting:
-
Calcination is heating in absence of air (used for carbonate ores).
-
Roasting is heating in presence of air (used for sulphide ores).
Example:
-
Reduction:
Metal oxides are reduced using carbon, aluminum, or electrolytic methods.
Example:
-
Purification:
Extracted metal is refined using electrolysis or distillation.
हिंदी में:
धातुओं को अयस्कों से प्राप्त करने की प्रक्रिया में कई चरण होते हैं:
-
अयस्क की सांद्रता:
गैंग (गैर जरूरी सामग्री) को हटाया जाता है। इसके लिए गुरुत्व पृथक्करण, फेना तैरन विधि, चुंबकीय पृथक्करण का प्रयोग होता है। -
उष्माजनन या भर्जन (Calcination/Roasting):
-
उष्माजनन: बिना वायु के ताप देना (कार्बोनेट अयस्क के लिए)
-
भर्जन: वायु में ताप देना (सल्फाइड अयस्क के लिए)
उदाहरण:
-
अपचयन (Reduction):
धातु के ऑक्साइड को कार्बन, एल्युमिनियम या विद्युत अपघटन द्वारा घटाया जाता है।
-
शुद्धिकरण:
निकाली गई धातु को इलेक्ट्रोलिसिस या आसवन द्वारा शुद्ध किया जाता है।
🔶 Q9. Compare the physical properties of metals and non-metals. / धातु और अधातु के भौतिक गुणों की तुलना कीजिए।
Answer / उत्तर:
| Property | Metals | Non-metals |
|---|---|---|
| Luster | Shiny (e.g., gold, silver) | Dull (e.g., sulfur, phosphorus) |
| Malleability | Can be beaten into sheets | Brittle, break on hammering |
| Ductility | Can be drawn into wires | Not ductile |
| Conductivity | Good conductor of heat & electricity | Poor conductor (except graphite) |
| State | Mostly solid | Solid, liquid, or gas |
| Sonority | Produce sound when struck | Do not produce sound |
हिंदी में:
| गुण | धातु | अधातु |
|---|---|---|
| चमक (Luster) | चमकदार (जैसे सोना, चाँदी) | मटमैले (जैसे गंधक, फास्फोरस) |
| तन्यता (Malleability) | पीटे जा सकते हैं | आसानी से टूट जाते हैं |
| नलीत्व (Ductility) | तार में बदले जा सकते हैं | नहीं बदले जा सकते |
| चालकता | गर्मी व विद्युत के अच्छे चालक | खराब चालक (ग्रेफाइट को छोड़कर) |
| अवस्था | अधिकतर ठोस | ठोस, द्रव या गैस |
| ध्वन्यता (Sonority) | चोट करने पर ध्वनि उत्पन्न करते हैं | ध्वनि उत्पन्न नहीं करते |
🔶 Q10. Why are metals used in electrical wires and cooking utensils? / विद्युत तारों और बर्तन बनाने में धातु का उपयोग क्यों होता है?
Answer / उत्तर:
Metals are widely used in electrical wiring and cooking utensils due to their physical and chemical properties.
-
Electrical Wires:
Metals like copper and aluminum are excellent conductors of electricity. They have:
-
Low resistance
-
High ductility (can be drawn into thin wires)
-
Do not react easily with environment
Hence, they are used in electric circuits and wiring.
-
Cooking Utensils:
Metals like aluminum, copper, and stainless steel:
-
Conduct heat efficiently
-
Have high melting points
-
Do not react with food easily
-
Are strong and durable
Thus, metals are ideal for use in kitchens and industries.
हिंदी में:
धातुओं का उपयोग विद्युत तारों और रसोई बर्तनों में उनके विशेष गुणों के कारण किया जाता है।
-
विद्युत तारों में:
ताँबा और एल्युमिनियम जैसे धातु बहुत अच्छे विद्युत चालक होते हैं।
-
इनमें प्रतिरोध कम होता है
-
ये तारों में खिंच सकते हैं
-
वातावरण से जल्दी नहीं घिसते
इसलिए इन्हें विद्युत सर्किटों में प्रयोग किया जाता है।
-
रसोई के बर्तनों में:
एलुमिनियम, तांबा और स्टेनलेस स्टील जैसे धातु:
-
अच्छी तरह गर्मी का संचार करते हैं
-
उच्च गलनांक वाले होते हैं
-
भोजन से प्रतिक्रिया नहीं करते
-
मज़बूत और टिकाऊ होते हैं
इसलिए इनका उपयोग रसोई और उद्योगों में किया जाता है।
KUCH QUESTION JO EXAM ME IMPORTANT HOTE HAI.
कृपया दिए गए प्रश्नों के उत्तर कमेंट में प्रश्न संख्या लिखकर बताएं कि आपके अनुसार सही उत्तर क्या हैं।
Please write your answers in the comments by mentioning the question number and the option you think is correct
निम्नलिखित में से किस धातु को मिट्टी के तेल में रखा जाता है?
Which of the following metals is stored in kerosene oil?
(a) एल्युमिनियम (Aluminium)
(b) तांबा (Copper)
(c) सोडियम (Sodium)
(d) लोहा (Iron)
-
निम्न में से कौन-सी धातु सबसे अच्छा विद्युत चालक है?
Which of the following is the best conductor of electricity?
(a) चांदी (Silver)
(b) लोहा (Iron)
(c) पारा (Mercury)
(d) जिंक (Zinc)
-
अधातुएं सामान्यतः कैसी होती हैं?
Non-metals are generally:
(a) तन्य (Ductile)
(b) घनघनाहट वाली (Sonorous)
(c) भंगुर (Brittle)
(d) चमकदार (Lustrous)
-
पीने के पानी की सफाई में निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सा अधातु प्रयोग होता है?
Which of the following non-metals is used in the disinfection of drinking water?
(a) फॉस्फोरस (Phosphorus)
(b) सल्फर (Sulphur)
(c) क्लोरीन (Chlorine)
(d) आयोडीन (Iodine)
-
निम्न में से कौन-सी धातु सामान्य तापमान पर द्रव रूप में होती है?
Which of these metals is liquid at room temperature?
(a) पारा (Mercury)
(b) सीसा (Lead)
(c) जिंक (Zinc)
(d) निकल (Nickel)
-
निम्नलिखित में से सबसे अभिक्रियाशील धातु कौन-सी है?
Which metal is most reactive among the following?
(a) सोना (Gold)
(b) मैग्नीशियम (Magnesium)
(c) चांदी (Silver)
(d) प्लेटिनम (Platinum)
-
पौधों में प्रकाश संश्लेषण के लिए आवश्यक अधातु कौन-सा है?
Which of the following non-metals is essential for plants in the process of photosynthesis?
(a) हाइड्रोजन (Hydrogen)
(b) नाइट्रोजन (Nitrogen)
(c) ऑक्सीजन (Oxygen)
(d) कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड (Carbon dioxide)
-
निम्न में से कौन-सा धातु की रासायनिक विशेषता नहीं है?
Which of the following is not a chemical property of metals?
(a) ऑक्साइड बनाना (Formation of oxides)
(b) अम्ल बनाना (Formation of acids)
(c) विस्थापन अभिक्रिया (Displacement reaction)
(d) जल के साथ अभिक्रिया (Reaction with water)
-
जब सल्फर डाइऑक्साइड को पानी में घोला जाता है तो क्या होता है?
What happens when sulphur dioxide is dissolved in water?
(a) क्षारीय घोल बनता है (Basic solution is formed)
(b) नमक बनता है (Salt is formed)
(c) अम्लीय घोल बनता है (Acidic solution is formed)
(d) कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होता (No change)
-
निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सा अधातु अर्धचालक (semiconductor) बनाने में प्रयोग होता है?
Which one of the following is used in making semiconductors?
(a) सिलिकॉन (Silicon)
(b) लोहा (Iron)
(c) एल्युमिनियम (Aluminium)
(d) तांबा (Copper)
11 Which of the following metals is the poorest conductor of heat?
निम्न में से कौन-सी धातु सबसे खराब ताप चालक है?-
(a) Lead
-
(b) Iron
-
(c) Aluminium
-
(d) Silver
-
-
12 Which metal is commonly used to make aircraft bodies?
किस धातु का प्रयोग सामान्यतः हवाई जहाज के शरीर बनाने में किया जाता है?-
(a) Copper
-
(b) Aluminium
-
(c) Zinc
-
(d) Steel
-
-
13 Which non-metal is used in the preparation of antiseptics?
किस अधातु का प्रयोग जीवाणुनाशक (antiseptic) बनाने में किया जाता है?-
(a) Chlorine
-
(b) Sulphur
-
(c) Iodine
-
(d) Oxygen
-
-
14 Which of these is a non-metal but conducts electricity?
इनमें से कौन-सा अधातु है लेकिन विद्युत का संचालन करता है?-
(a) Sulphur
-
(b) Graphite
-
(c) Bromine
-
(d) Phosphorus
-
-
15 Which metal is used in bells and statues due to its sonorous property?
किस धातु का उपयोग घंटियों और मूर्तियों में इसकी ध्वनि गुण के कारण किया जाता है?-
(a) Bronze
-
(b) Aluminium
-
(c) Iron
-
(d) Zinc
-
-
16 Which non-metal is used in making fertilizers?
किस अधातु का उपयोग उर्वरक बनाने में किया जाता है?-
(a) Phosphorus
-
(b) Oxygen
-
(c) Iodine
-
(d) Helium
-
-
17 Which of the following does not react with cold water but reacts with steam?
निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सी धातु ठंडे पानी से नहीं पर भाप से प्रतिक्रिया करती है?-
(a) Magnesium
-
(b) Sodium
-
(c) Calcium
-
(d) Iron
-
-
18 Which of the following is not a physical property of metals?
निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सा धातुओं का भौतिक गुण नहीं है?-
(a) Malleability
-
(b) Ductility
-
(c) Brittle nature
-
(d) Lustre
-
-
19 Which non-metal exists in liquid state at room temperature?
कौन-सा अधातु सामान्य तापमान पर द्रव अवस्था में पाया जाता है?
-
(a) Chlorine
-
(b) Bromine
-
(c) Iodine
-
(d) Nitrogen
10.10Which non-metal is stored in water to prevent its reaction with air?
किस अधातु को हवा से प्रतिक्रिया से बचाने के लिए पानी में रखा जाता है?
-
(a) Sulphur
-
(b) Phosphorus
-
(c) Carbon
-
(d) Iodine
## 📌💁 *निष्कर्ष | Conclusion*
धातु और अधातु विज्ञान के मूलभूत तत्व हैं। इनके गुण और उपयोग को समझना हमारे दैनिक जीवन और परीक्षाओं दोनों के लिए बहुत उपयोगी है।
*Metals and non-metals are fundamental elements of science. Understanding their properties and uses is helpful for daily life and for exams.
🙏🙏THANK YOU🙏🙏
अगर आपको यह पोस्ट पसंद आई हो तो कृपया कमेंट करें और ब्लॉग को फॉलो करना न भूलें। आपके कमेंट और फॉलो से हमें प्रोत्साहन मिलता है और हम और भी अच्छा कंटेंट लाने के लिए प्रेरित होते हैं।
If you found this post helpful, please leave a comment and don’t forget to follow the blog. Your support encourages us to create more valuable content.





कोई टिप्पणी नहीं:
एक टिप्पणी भेजें